✕
459 results
How Covid Shook the World s Economy Deftly weaving finance politics business and the global human experience into one tight narrative a tour de force account of 2020 the year that changed everything from the acclaimed author of Crashed The shocks of 2020 have been great and small disrupting the …
A Theory From bestselling writer David Graeber a master of opening up thought and stimulating debate Slate a powerful argument against the rise of meaningless unfulfilling jobs and their consequences Does your job make a meaningful contribution to the world In the spring of 2013 David Graeber asked this question …
In this volume, Katz offers a detailed summary of the foundations, evolutions and approaches of Dependency Theory in Latin America, focusing on the regional interpretations of Marxism, Developmentalism and World-Systems Theory.
To grasp sex in all its complexity, including its relationship to gender, class, race and power, Srinivasan argues that we need to move beyond the simplistic views of consent in the form of yes-no, to rather consider the more complex question of wanted-unwanted.
Identity politics is everywhere, polarising discourse from the campaign trail to the classroom and amplifying antagonisms in the media. But the compulsively referenced phrase bears little resemblance to the concept as first introduced by the radical Black feminist Combahee River Collective.
In this lecture, Sanjay Reddy reviews the work of János Kornai, especially his critique of the socialist system, which is rooted in his understanding of the eminently political character of socialism.
The idea of a Green New Deal was launched into popular consciousness by US Congressperson Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez in 2018. Evocative of the far-reaching ambitions of its namesake, it has become a watchword in the current era of global climate crisis. But its new ubiquity brings ambiguity: what - and for whom - is the Green New Deal?
Karl William Kapp (1910-1976) was one of the forefathers of Ecological Economics. Influenced namely by the Frankfurt School, Institutionalist Economics and Pragmatist Philosophy, he contributed to debates on the social costs of production, economic planning, sustainable development and epistemology. I
To explain the pronounced instability of the world economy since the 1970s, the book offers an important and systematic theoretical examination of money and finance.
The world's leading economist of inequality presents a short but sweeping and surprisingly optimistic history of human progress toward equality despite crises, disasters, and backsliding.
Money is the fantasy that makes the world go round. Where did it come from and what is its future? From the Bank of England to Bitcoin and the Bristol Pound, LSE sociologist Nigel Dodd explores.
What is economics? What can - and can't - it explain about the world? Why does it matter?
This brilliantly concise book is a classic introduction to Marx’s key work, Capital. In print now for over a quarter of a century, and previously translated into many languages, the new edition has been fully revised and updated, making it an ideal modern introduction to one of the most important texts in political economy.
Financialization is one of the most innovative concepts to emerge in the field of political economy during the last three decades, although there is no agreement on what exactly it is. Profiting Without Producing by Costas Lapavitsas puts forth a distinctive view defining financialization in terms of the fundamental conduct of non-financial enterprises, banks and households.
Economics for Emancipation (E4E) is a seven-module introductory curriculum with interactive and participatory workshops. It offers a deep critical dive into the current political economic system, exploration of alternative economic systems, and dynamic tools to dream and build the economy that centers care, relationship, and liberation.
In Colonial Debts Rocío Zambrana develops the concept of neoliberal coloniality in light of Puerto Rico's debt crisis. Drawing on decolonial thought and praxis, Zambrana shows how debt functions as an apparatus of predation that transforms how neoliberalism operates.
What are the implications of the politics of "behavioural change"? Alexander Feldmann took a closer look for you on nudging and framing and if this is a legitimate instrument being used by the state to make us behave better in terms of our carbon footprint.
An essay of the writing workshop on contemporary issues in the field of Nigerian economics: In Nigeria, it appears that there is nothing in the constitution, which excludes the participation of women in politics. Yet, when it comes to actual practice, there is extensive discrimination. The under-representation of women in political participation gained root due to the patriarchal practice inherent in our society, much of which were obvious from pre-colonial era till date.
The core of Georgism is a policy known as the Land Value Tax (LVT), a policy which Georgists claim will solve many of society and the economy’s ills. Georgism is an interesting school of thought because it has the twin properties that (1) despite a cult following, few people in either mainstream or (non-Georgist) heterodox economics pay it much heed; (2) despite not paying it much heed, both mainstream and heterodox economists largely tend to agree with Georgists. I will focus on the potential benefits Georgists argue an LVT will bring and see if they are borne out empirically. But I will begin by giving a nod to the compelling theoretical and ethical dimensions of George’s analysis, which are impossible to ignore.
Environmental catastrophe looms large over politics: from the young person’s climate march to Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez’s Green New Deal, increasing amounts of political space are devoted to the issue. Central to this debate is the question of whether economic growth inevitably leads to environmental issues such as depleted finite resources and increased waste, disruption of natural cycles and ecosystems, and of course climate change. Growth is the focal point of the de-growth and zero-growth movements who charge that despite efficiency gains, increased GDP always results in increased use of energy and emissions. On the other side of the debate, advocates of continued growth (largely mainstream economists) believe that technological progress and policies can ‘decouple’ growth from emissions.
How countries achieve long-term GDP growth is up there with the most important topics in economics. As Nobel Laureate Robert Lucas put it “the consequences for human welfare involved in questions like these are simply staggering: once one starts to think about them, it is hard to think about anything else.” Ricardo Hausmann et al take a refreshing approach to this question in their Atlas of Economic Complexity. They argue a country’s growth depends on the complexity of its economy: it must have a diverse economy which produces a wide variety of products, including ones that cannot be produced much elsewhere. The Atlas goes into detail on exactly what complexity means, how it fits the data, and what this implies for development. Below I will offer a summary of their arguments, including some cool data visualisations.
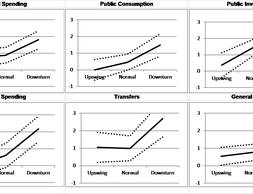
What influence do changes in tax policy or state decisions on expenditure have on economic growth? For decades, this question has been controversially debated.
An essay of the writing workshop on Nigeria’s Readiness for and the Effect of the Fourth Industrial Revolution
Recovery from the Covid-19 crisis provides a chance to implement economic measures that are also beneficial from environmental and social perspectives. While ‘green’ recovery packages are crucial to support economies tracking a low-carbon transition in the short-term, green measures such as carbon pricing are also key to improving welfare in the long-term. This commentary specifies the need for carbon pricing, outlines its implications for our everyday lives, and explains how it works alongside value-based change in the context of climate action and societal well-being.
This syllabus provides an overview of the contents of the course "Understanding Economic Models" at the University of Helsinki.
Learn the basics of microeconomics including supply and demand of commodities and how equilibrium in the market affects price Joon Koo Lee edX Seoul National University
The core idea of ecological economics is that human economic activity is bound by absolute limits. Interactions between the economy, society and the environment are analysed, while always keeping in mind the goal of a transition towards sustainability.
Isabella M Weber and Evan Wasner challange the dominant view of inflation that it is macroeconomic in origin and must always be tackled with macroeconomic tightening In contrast they argue that inflation is predominantly a sellers inflation that derives from microeconomic origins namely the ability of firms with market power …
Happy International Women s Day This International Women s Day 2018 is an opportune moment to highlight prominent scholars of Feminist Economics As a subdiscipline of economics Feminist Economics analyzes the interrelationship between gender and the economy often critiquing inequities and injustices perpetuated by mainstream paradigms Work of this nature …
Currency hierarchy and policy space: A research agenda for development economics Barbara Fritz
This Forum in the Boston Review deals with the role of economics in modern policymaking and presents a wide set of perspectives on the topic. The opening text by Suresh Naidu, Dani Rodrik and Gabriel Zucman aims to answer a range of common criticisms against the modern, neoclassical science of economics and its influence on public discussions.
Nathan Tankus created this series to introduce people outside of the inner financial circles of professionals, journalists and policymakers to the basic mechanisms and dynamics of monetary policy.
We use cookies on our website. Click on Accept to help us to make Exploring Economics constantly better!